About image specifications



When preparing to submit images for publication on websites and magazines you will usually have been given precise specifications for the images in the form of properties such as file format (e.g. jpg), pixel dimensions, dpi, etc.
There are 6 different properties used to specify a digital image but as they are inter-related you may only be given two or three of them.
To explain two of them very simply:
- Pixels are the coloured dots that make up an image. The more pixels, the bigger the image will appear on screen and when printed.
- Dpi (dots per image) is a measure of how close together the pixels are printed/displayed.
- A computer printer prints at 300dpi which is close enough for the eye not to see the gaps between the dots.
- A computer screen typically displays at 72dpi. As the pixels glow, the eye doesn’t see the gaps between them.
The following explains all six properties in detail. Click each property for an explanation.
How to change image properties (pixels, size, dpi, etc.)
Changing the properties of an image is best done using a specialist graphics program such as Photoshop or Paintshop Pro.
However Windows and Mac computers come with free graphics programs (such Microsoft Paint on Windows and Preview on Macs) which can also be used but they are not as powerful as a specialist graphics program.
Windows users in particular should download paint.NET (download free from www.getpaint.net) in order to be able to change dpi as Microsoft Paint only enables you to change image dimensions.
The following section explains the general principles of changing image properties and applies to most makes of graphics programs.
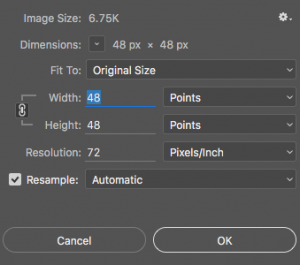
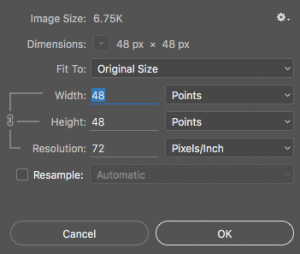
To change properties you will need to find the graphics program’s ‘Image Size’ tool.
Graphics programs have a menu option such as ‘Image Size’ (under ‘Image’ in Photoshop) or ‘Adjust Size’ (under ‘Tools’ in Mac Preview) or ‘Resize’ (under ‘Image’ in Paint.NET).
Select this menu option to start the re-size tool.
Explanations of other key concepts of image manipulation
File sizes of images – Tif images
The file size of an image is determined by a number of factors:
- The number of pixels in the image
- The format the image has been saved with (e.g. jpg or tif)
- If a jpg, then the quality the jpg has been saved at and the complexity of the image
File Sizes of images – JPG images
The jpg image file type was created in order to reduce the file size of images. It compresses the image data by specially encoding it using various procedures. Jpgs are typically about 10% of the size of the tif version.
 The pixel dimensions of an image are the number of coloured dots or pixels horizontally and vertically that form the image. 1024 x 768 means there are 1024 dots horizontally and 768 vertically – a total of 1024 x 768 = 786,432 pixels.
The pixel dimensions of an image are the number of coloured dots or pixels horizontally and vertically that form the image. 1024 x 768 means there are 1024 dots horizontally and 768 vertically – a total of 1024 x 768 = 786,432 pixels.
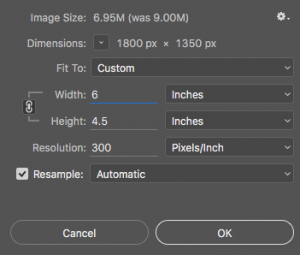
 The size of a printed image is determined by its pixel dimensions and its resolution.
The size of a printed image is determined by its pixel dimensions and its resolution.